Implementing Subplots to our Chart with Matplotlib
In this Matplotlib tutorial, we'll be handling our previous tutorial's code, and implementing the subplot configuration from the previous tutorial. Our starting code:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
import matplotlib.ticker as mticker
from matplotlib.finance import candlestick_ohlc
from matplotlib import style
import numpy as np
import urllib
import datetime as dt
style.use('fivethirtyeight')
print(plt.style.available)
print(plt.__file__)
def bytespdate2num(fmt, encoding='utf-8'):
strconverter = mdates.strpdate2num(fmt)
def bytesconverter(b):
s = b.decode(encoding)
return strconverter(s)
return bytesconverter
def graph_data(stock):
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = plt.subplot2grid((1,1), (0,0))
stock_price_url = 'http://chartapi.finance.yahoo.com/instrument/1.0/'+stock+'/chartdata;type=quote;range=1m/csv'
source_code = urllib.request.urlopen(stock_price_url).read().decode()
stock_data = []
split_source = source_code.split('\n')
for line in split_source:
split_line = line.split(',')
if len(split_line) == 6:
if 'values' not in line and 'labels' not in line:
stock_data.append(line)
date, closep, highp, lowp, openp, volume = np.loadtxt(stock_data,
delimiter=',',
unpack=True,
converters={0: bytespdate2num('%Y%m%d')})
x = 0
y = len(date)
ohlc = []
while x < y:
append_me = date[x], openp[x], highp[x], lowp[x], closep[x], volume[x]
ohlc.append(append_me)
x+=1
candlestick_ohlc(ax1, ohlc, width=0.4, colorup='#77d879', colordown='#db3f3f')
for label in ax1.xaxis.get_ticklabels():
label.set_rotation(45)
ax1.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%Y-%m-%d'))
ax1.xaxis.set_major_locator(mticker.MaxNLocator(10))
ax1.grid(True)
bbox_props = dict(boxstyle='round',fc='w', ec='k',lw=1)
ax1.annotate(str(closep[-1]), (date[-1], closep[-1]),
xytext = (date[-1]+4, closep[-1]), bbox=bbox_props)
## # Annotation example with arrow
## ax1.annotate('Bad News!',(date[11],highp[11]),
## xytext=(0.8, 0.9), textcoords='axes fraction',
## arrowprops = dict(facecolor='grey',color='grey'))
##
##
## # Font dict example
## font_dict = {'family':'serif',
## 'color':'darkred',
## 'size':15}
## # Hard coded text
## ax1.text(date[10], closep[1],'Text Example', fontdict=font_dict)
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price')
plt.title(stock)
#plt.legend()
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.11, bottom=0.24, right=0.90, top=0.90, wspace=0.2, hspace=0)
plt.show()
graph_data('EBAY')
The first major change is to modify the axis definitions:
ax1 = plt.subplot2grid((6,1), (0,0), rowspan=1, colspan=1)
plt.title(stock)
ax2 = plt.subplot2grid((6,1), (1,0), rowspan=4, colspan=1)
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price')
ax3 = plt.subplot2grid((6,1), (5,0), rowspan=1, colspan=1)
Now, ax2 is where we'll actually be plotting our stock price data. The top and bottom charts will serve as indicator information shortly.
Further down in the code where we plot data, we need to change ax1 to ax1:
candlestick_ohlc(ax2, ohlc, width=0.4, colorup='#77d879', colordown='#db3f3f')
for label in ax2.xaxis.get_ticklabels():
label.set_rotation(45)
ax2.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%Y-%m-%d'))
ax2.xaxis.set_major_locator(mticker.MaxNLocator(10))
ax2.grid(True)
bbox_props = dict(boxstyle='round',fc='w', ec='k',lw=1)
ax2.annotate(str(closep[-1]), (date[-1], closep[-1]),
xytext = (date[-1]+4, closep[-1]), bbox=bbox_props)
With these changes, the full code should be:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
import matplotlib.ticker as mticker
from matplotlib.finance import candlestick_ohlc
from matplotlib import style
import numpy as np
import urllib
import datetime as dt
style.use('fivethirtyeight')
print(plt.style.available)
print(plt.__file__)
def bytespdate2num(fmt, encoding='utf-8'):
strconverter = mdates.strpdate2num(fmt)
def bytesconverter(b):
s = b.decode(encoding)
return strconverter(s)
return bytesconverter
def graph_data(stock):
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = plt.subplot2grid((6,1), (0,0), rowspan=1, colspan=1)
plt.title(stock)
ax2 = plt.subplot2grid((6,1), (1,0), rowspan=4, colspan=1)
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price')
ax3 = plt.subplot2grid((6,1), (5,0), rowspan=1, colspan=1)
stock_price_url = 'http://chartapi.finance.yahoo.com/instrument/1.0/'+stock+'/chartdata;type=quote;range=1m/csv'
source_code = urllib.request.urlopen(stock_price_url).read().decode()
stock_data = []
split_source = source_code.split('\n')
for line in split_source:
split_line = line.split(',')
if len(split_line) == 6:
if 'values' not in line and 'labels' not in line:
stock_data.append(line)
date, closep, highp, lowp, openp, volume = np.loadtxt(stock_data,
delimiter=',',
unpack=True,
converters={0: bytespdate2num('%Y%m%d')})
x = 0
y = len(date)
ohlc = []
while x < y:
append_me = date[x], openp[x], highp[x], lowp[x], closep[x], volume[x]
ohlc.append(append_me)
x+=1
candlestick_ohlc(ax2, ohlc, width=0.4, colorup='#77d879', colordown='#db3f3f')
for label in ax2.xaxis.get_ticklabels():
label.set_rotation(45)
ax2.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%Y-%m-%d'))
ax2.xaxis.set_major_locator(mticker.MaxNLocator(10))
ax2.grid(True)
bbox_props = dict(boxstyle='round',fc='w', ec='k',lw=1)
ax2.annotate(str(closep[-1]), (date[-1], closep[-1]),
xytext = (date[-1]+4, closep[-1]), bbox=bbox_props)
## # Annotation example with arrow
## ax1.annotate('Bad News!',(date[11],highp[11]),
## xytext=(0.8, 0.9), textcoords='axes fraction',
## arrowprops = dict(facecolor='grey',color='grey'))
##
##
## # Font dict example
## font_dict = {'family':'serif',
## 'color':'darkred',
## 'size':15}
## # Hard coded text
## ax1.text(date[10], closep[1],'Text Example', fontdict=font_dict)
#
#plt.legend()
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.11, bottom=0.24, right=0.90, top=0.90, wspace=0.2, hspace=0)
plt.show()
graph_data('EBAY')
The resulting graph should be:
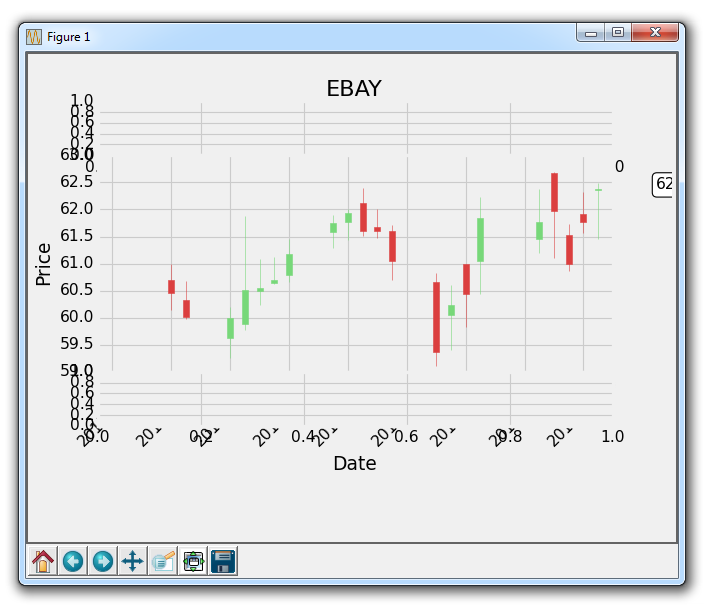
-
Introduction to Matplotlib and basic line
-
Legends, Titles, and Labels with Matplotlib
-
Bar Charts and Histograms with Matplotlib
-
Scatter Plots with Matplotlib
-
Stack Plots with Matplotlib
-
Pie Charts with Matplotlib
-
Loading Data from Files for Matplotlib
-
Data from the Internet for Matplotlib
-
Converting date stamps for Matplotlib
-
Basic customization with Matplotlib
-
Unix Time with Matplotlib
-
Colors and Fills with Matplotlib
-
Spines and Horizontal Lines with Matplotlib
-
Candlestick OHLC graphs with Matplotlib
-
Styles with Matplotlib
-
Live Graphs with Matplotlib
-
Annotations and Text with Matplotlib
-
Annotating Last Price Stock Chart with Matplotlib
-
Subplots with Matplotlib
-
Implementing Subplots to our Chart with Matplotlib
-
More indicator data with Matplotlib
-
Custom fills, pruning, and cleaning with Matplotlib
-
Share X Axis, sharex, with Matplotlib
-
Multi Y Axis with twinx Matplotlib
-
Custom Legends with Matplotlib
-
Basemap Geographic Plotting with Matplotlib
-
Basemap Customization with Matplotlib
-
Plotting Coordinates in Basemap with Matplotlib
-
3D graphs with Matplotlib
-
3D Scatter Plot with Matplotlib
-
3D Bar Chart with Matplotlib
-
Conclusion with Matplotlib
